Which is odd one 1 Stomata , reticulate venation , transpiration , chlorophyll , tendril 2 Sepals , petal , stamen , pistil ,petiol;Adventitious roots of sufficient length and diameter must develop to assure that the photosynthetic surfaces receive sufficient water and nutrients before grass seedlings can be considered establishedWhat is a tap root?
Logical Class Home
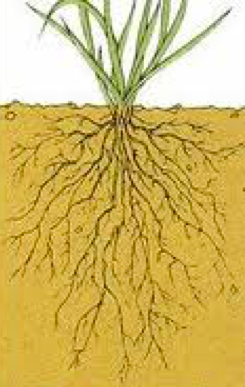
Grass adventitious roots
Grass adventitious roots-Adventitious roots are produced from shoot cells These form when stem cells or axillary buds change purpose and divide into root tissue Adventitious root growth is often spurred by low oxygen environments or high ethylene conditions Adventitious stems provide an important method of cloning and propagating various plantsFibrous roots have a bushy appearance and consists of thin root fibres Example Wheat, rice, maize grass etc Adventitious root system In this type, massive root growth appears from any part of the plant body other than the primary root Example Banyan, Monstera etc Characteristics A root system possesses the following key characteristics
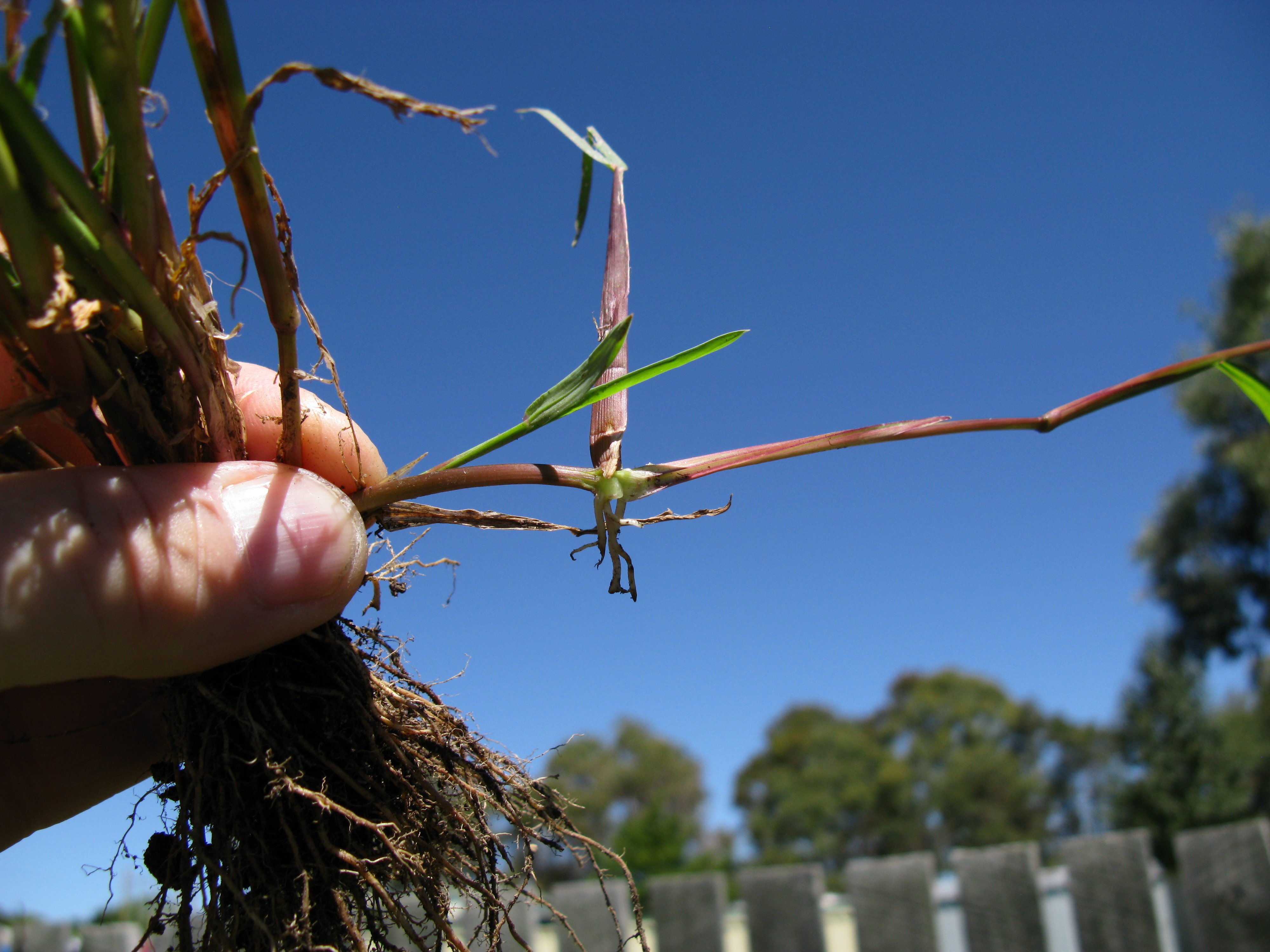



File Echinochloa Colona Adventitious Root Jpg Wikimedia Commons
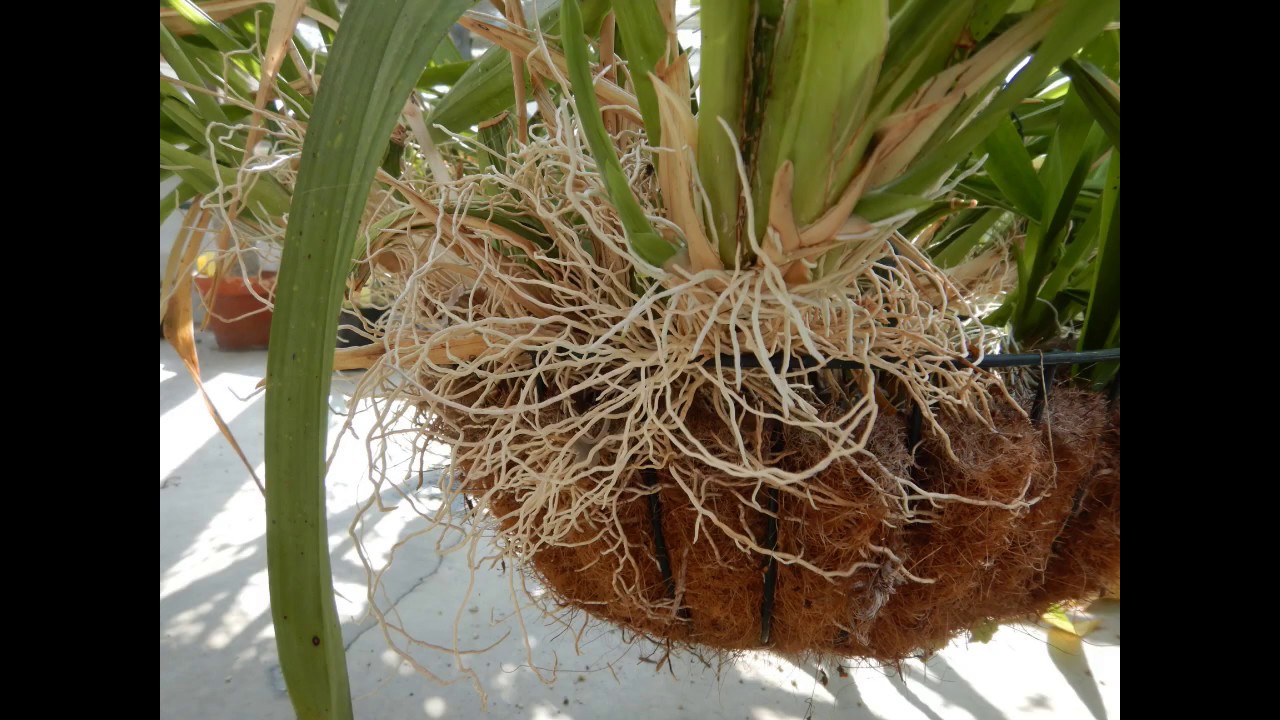
Adventitious Roots Arising From Stems Left Red mangrove ( Rhizophora mangle ) growing in seawater along the shoreline of St John (US Virgin Islands) The adventitious prop roots help to support and securely anchor this shrub in the mud and loose sand of tidal watersAdventitious roots were observed on 90% of the crested wheat grass seedlings and 100% of the blue grama seedlings during the week of 30 July, 14 days after emergence (Figs 4 and 5)Adventitious roots are the roots of the mature grass plant The seminal roots will disappear The roots anchor the plant to the ground, absorb nutrients and water from the soil, and function as carbohydrate storage tanks (Fig 6, root diagram)
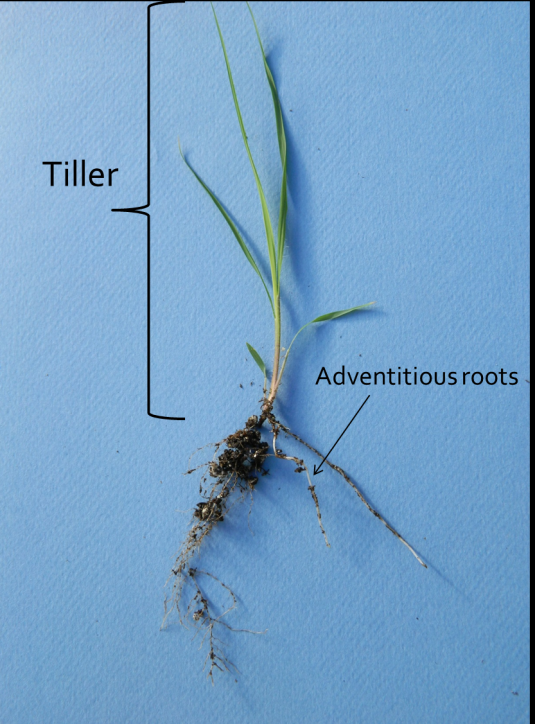
While both seminal and adventitious roots (image on right) may be observed growing from turfgrass plants, the root system associated with a mature turfgrass community is expected to be entirely adventitious These roots grow from crowns as well as nodes along rhizomes and stolons M35 Roots Root Tip The root is composed of an organized arrangement of cells produced by division of meristimatic cells located behind the root cap This is shown on the illustration to the rightThese primary roots are then replaced by the second type of root system found in Grasses, that is, adventitious root system Adventitious Root System of Grass plants The adventitious root system is that system in which roots develop from the nodes of the crown and lateral stems It is a replacement of the primary root system in Grasses The adventitious root system functions throughout the lifetime of the shoot, however, the longevity is ruled partially by defoliation management as well asAdventitious Roots formed from areas of the plant other than the root meristem, generally from the stem Grass Identification Tips Because the leaves and flowers of grasses can often look similar to one another, being able to identify the unique anatomical features that can be used to differentiate between the various grass genera and
It is the root system that develops from any part of the plant other than the radicle – usually a stem and sometimes a leaf The adventitious roots are found in monocot plants where the taproot is shortlived Examples Grass, sugarcane, oak, and ivy Based on the origin of the adventitious root, they are further classified into a) Fibrous RootsThese roots originate from the base of the stem and constitute the fibrous root system, as seen in the wheat plant In some plants, like grass, Monstera and the banyan tree, roots arise from parts of the plant other than the radicle and are called adventitious rootsAdventitious root system may be underground or aerial They generally develop from stem nodes, intermodals, leaves, etc Horizontal stem of creepers often develop adventitious roots from the nodes (eg, Grass, Wood Sorrel) Branch cuttings and leaf cuttings (eg, Rose, Sugarcane, Tapicca, Sansiviena) develop adventitious roots when placed in soil In Coleus, the cuttings develop adventitious roots on being partially immersed in water



File Echinochloa Colona Adventitious Root Jpg Wikimedia Commons



Pca Alien Plant Working Group West Indian Marsh Grass Hymenachne Amplexicaulis
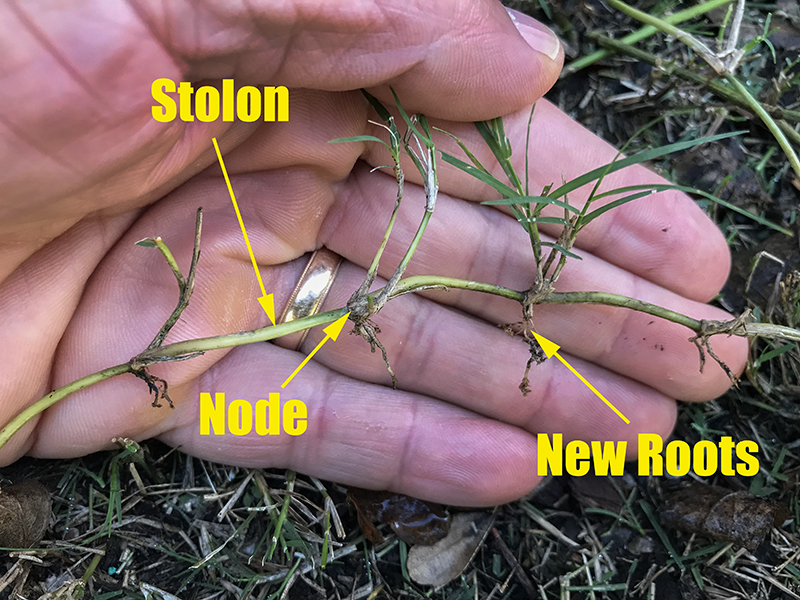
Adventitious roots develop from the coleoptilar node if moist conditions exist for several days (Moser and Newman 19) Roots may reach depths of 2 to 4 feet at the end of establishment yearThese grasses have primary and secondary root systems The primary roots (AKA seminal roots) are adapted to absorb water and nutrients as the grass is established;• Adventitious stems – either rhizomes or stolons STOLON • Stolons (runners) – above ground, horizontal stems with nodes, internodes and leaves • Rhizomes – underground, horizontal stems;



Turfgrass Physiology



Which Of The Following Is An Example Of A Modified Class 11 Biology Cbse
Adventitious roots within 6 to 10 weeks after emergence they often died Seedling death was caused by the expansion of leaf area beyond the ability of the seedlings seminal roots to provide adequate moisture Without adventitious root development an increased transpiration stress was causing seedling and stand mortality To developIs sweet potato a stem,a root,or a fruit?The adventitious nodal root system consists of whorls of roots originating from nodes along the base of the tiller forming the permanent root system of the grass plant Adventitious root longevities vary from 1 to 4 years among species (Weaver and Zink 1946, Troughton 1981)



Vegetative Terminology Part 1
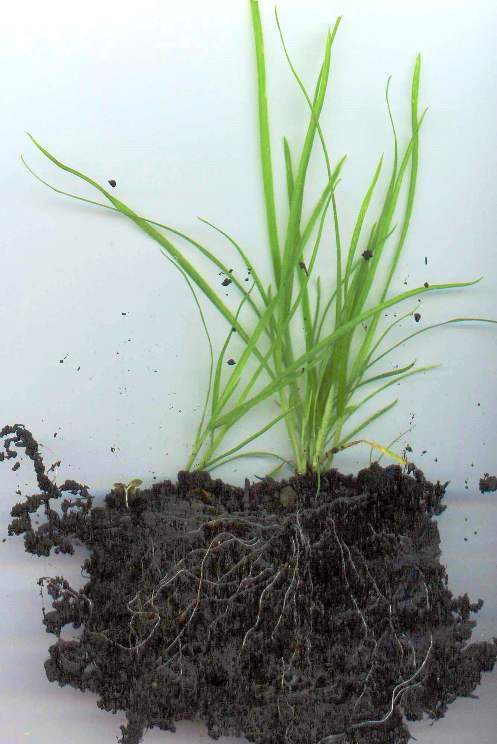



Grass Root System Studiousguy
Adventitious roots are generally seen growing from aerial parts of the plants They can arise from injured roots, stem, internodes, branches, or any other tissue They are formed from the preinduced root primordial cells Adventitious roots commonly occur in monocots but also in some dicots, such as Ivy, Strawberry, Clover, and WillowFibrous root Adventitious root The primary root is replaced by a large number of roots at its base of the stem to constitute the Fibrous roots The roots that arise from any part of the plant apart from radicle are called adventitious roots The examples of fibrous roots include wheat, rice etc The examples of plants with adventitious roots include grass, banyan tree, maize etc Q6Adventitious roots develop from the underground part of the plant, which is known as the layer This method of vegetative reproduction also occurs naturally Another similar method, air layering , involved the scraping and replanting of tree branches which develop into treesExampleJasmine and Bougainvillea


Tomato Adventitious Roots


Difference Between Taproot And Fibrous Root Difference Between
Adventitious roots and aerial shoots arise from nodes The terminal bud nested in the apex of the stolon may turn upward to form a new shoot or continue horizontal gowth Most stoloniferous grasses are considered invasive species Lateral spreading via stolons is characteristic of bermudagrass, zoysia, and buffalo grassC) True Adventitious Roots Lateral buds that arise from parts of the stem (at the nodes and internodes) are called true adventitious roots Examples Aerial roots of a banyan tree, stilt roots of sugarcane, and clasping roots of the money plantThese roots originate from the base of the stem and constitute the fibrous root system Adventitious root Adventitious roots do not develop from another root In some plants, like GRASS, MONSTERA and BANYAN TREE, many roots arise from parts of the plant (from a stem, leaf or other plant parts) other than the radicle These types of roots are called adventitious roots



Adventitious Roots On Corn Asparagus Roots Animals



Plant Lab 1c Grass Structure Diagram Quizlet
Give difference between tap root and fibrous root;Dicots have a tap root system which is the primary root system, while monocots have a fibrous root system that looks like fiber, and is also known as an adventitious root systemAdventitious roots are the type of roots that arise from parts of the plant other than the radicle These roots can arise from the injured root, nodes of the stem, internodes, branches, or any other tissue A mass of adventitious roots along with its branches constitutes an ' adventitious root system'



Phragmites Invasion Detrimental Or Beneficial


Morphology Modified Doc
The adventitious nodal root system consists of whorls of roots originating from nodes along the base of the tiller forming the permanent root system of the grass plant Adventitious root longevities vary from 1 to 4 years among species (Weaver and Zink 1946, Troughton 1981)Some roots, called adventitious roots, arise from an organ other than the root—usually a stem, sometimes a leaf They are especially numerous on underground stems, such as rhizomes, corms, and tubers, and make it possible to vegetatively propagate many plants from stem or leaf cuttingsSheath Base portion of the grass leaf that wraps around the stem Spike A type of flower in which the flower clusters are attached directly to the stem Stolon A stem that grows horizontally along the ground surface and may form adventitious roots and a new plant at the nodes



Grass Tree Description Facts Britannica


Botanical Illustration Exploring Root Variety Lizzie Harper
Adventitious roots and shallow root systems roots grow near the surface where they can obtain oxygen (examples mangroves) pneumatophores modified root systems, sometimes above ground, to increase respiration floating leaves leaves with a thick cuticle (skin) to prevent water penetration (examples lily pads)Primary root length was increased only by the volatile compounds emitted by Enterobacter cloacae JM22 and Bacillus pumilus T4 Overall, the most significant results were obtained with Bacillus subtilis GB03, which induced an 81 % increase in total biomass, as well as enhancing total root length, total secondary root length and total adventitious root length by 5, 15 and 4745 %, respectivelySheath Base portion of the grass leaf that wraps around the stem Spike A type of flower in which the flower clusters are attached directly to the stem Stolon A stem that grows horizontally along the ground surface and may form adventitious roots and a new plant at the nodes



Washington State Noxious Weed Control Board



How To Control Weeds Now For A Fabulous Fall Lawn Calloway S Nursery
(in words) why are petals colourful?Adventitious root system may be underground or aerial They generally develop from stem nodes, intermodals, leaves, etc Horizontal stem of creepers often develop adventitious roots from the nodes (eg, Grass, Wood Sorrel) Branch cuttings and leaf cuttings (eg, Rose, Sugarcane, Tapicca, Sansiviena) develop adventitious roots when placed in soil In Coleus, the cuttings develop adventitious roots on being partially immersed in waterThese are called aerial roots Alike underground roots, these aerial roots are also responsible for absorbing nutrients, anchoring and affixing the plant by supporting them to the structures such as nearby walls, rocks, trellises, etc Few examples of plants with the aerial roots are–Bonsai, Banyan Tree, Mangroves, etc



Adventitious Roots Aerial Roots Epiphytes Youtube



Plant Root Types Fibrous Root Vs Taproot System
Adventitious roots of sufficient length and diameter must develop to assure that the photosynthetic surfaces receive sufficient water and nutrients before grass seedlings can be considered establishedIn young stems, adventitious roots often form from parenchyma between the vascular bundles In stems with secondary growth, adventitious roots often originate in phloem parenchyma near the vascular cambium In stem cuttings, adventitious roots sometimes also originate in the callus cells that form at the cut surfaceRoots are the underground part, which helps in absorbing nutrients, water, and moisture from the soil Most flowering plants, shrubs, and trees produce tap roots which can travel deep into the soil, while fibrous or adventitious roots are seen in grasses and reed (tall grasses) plants and grow near to the surface of the soil
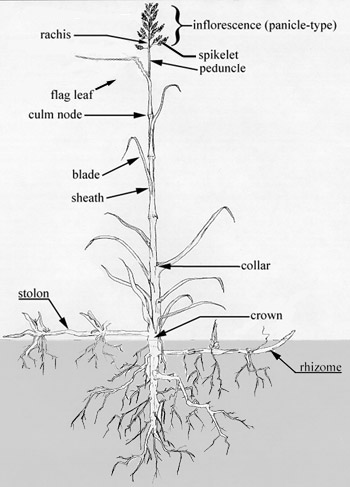


Rhizomes And Stolons Forage Information System Oregon State University



Taproot Vs Fibrous Root Definition 17 Major Differences Examples
These plants have trailing stem on which roots are present throughout For example, Oxalis, Cynodon (doob grass) Adventitious roots arise from nodes throughout the length of the stem, Trailers They resemble creepers but lack the adventitious roots does not arise from nodes Basella belongs to this group Climbers Pea plants belong to this groupAdventitious roots within 6 to 10 weeks after emergence they often died Seedling death was caused by the expansion of leaf area beyond the ability of the seedlings seminal roots to provide adequate moisture Without adventitious root development an increased transpiration stress was causing seedling and stand mortality To developThese are called aerial roots Alike underground roots, these aerial roots are also responsible for absorbing nutrients, anchoring and affixing the plant by supporting them to the structures such as nearby walls, rocks, trellises, etc Few examples of plants with the aerial roots are–Bonsai, Banyan Tree, Mangroves, etc
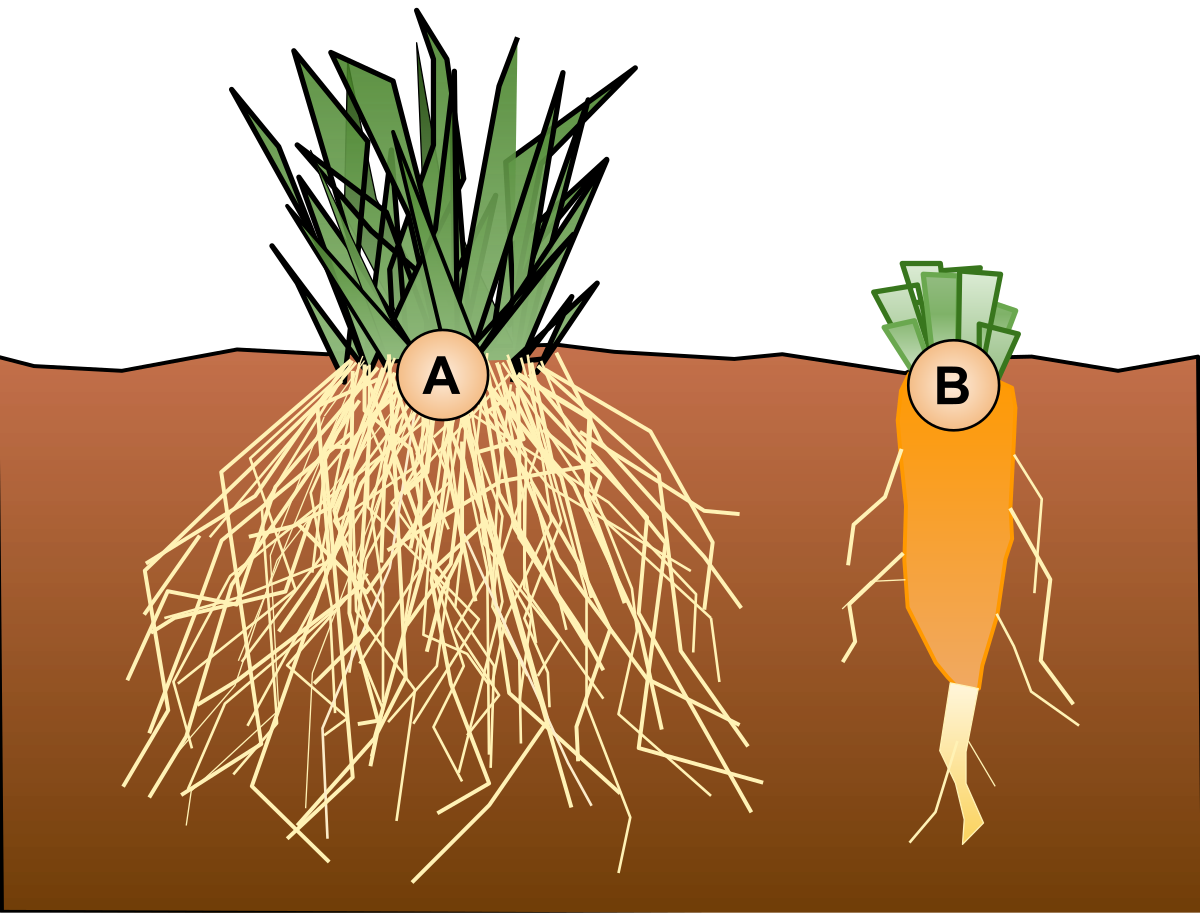


Taproot Wikipedia


Exe
Adventitious roots are still roots, and therefore, their main function is the absorption of minerals and water Their formation is basically a survival mechanism, and therefore, their primary duty is to supplement the main root when its functioning is impaired due to disease, damage, or otherwiseIs sweet potato a stem,a root,or a fruit?Later on, secondary roots (AKA adventitious roots) take over the majority of absorption



Logical Class Home



Japanese Stilt Grass Archives Plant Talk
Rhizome A stem that grows horizontally along the ground surface and may form adventitious roots at the nodes Sheath Base portion of the grass leaf that wraps around the stem Spike A type of flower in which the flower clusters are attached directly to the stemDifference Between Tap Root and Fibrous (Adventitious) Root The main root (primary root) with other minor side roots, which grow deep into the soil is called Taproot While the fine, thick hairs like structure, that spread sideways in all the directions is called Fibrous or Adventitious root Taproot arises from the radicle (embryonic part) of the plants, but the Fibrous root grows from the stem and leaves rather from the radicleAlthough the primary roots continue to function for up to a year after germination, water and nutrient uptake is gradually taken over by the secondary roots (sometimes referred to as adventitious roots) which become more numerous as the grass plant matures Secondary roots are produced from nodes in the crown or from nodes on horizontal stems
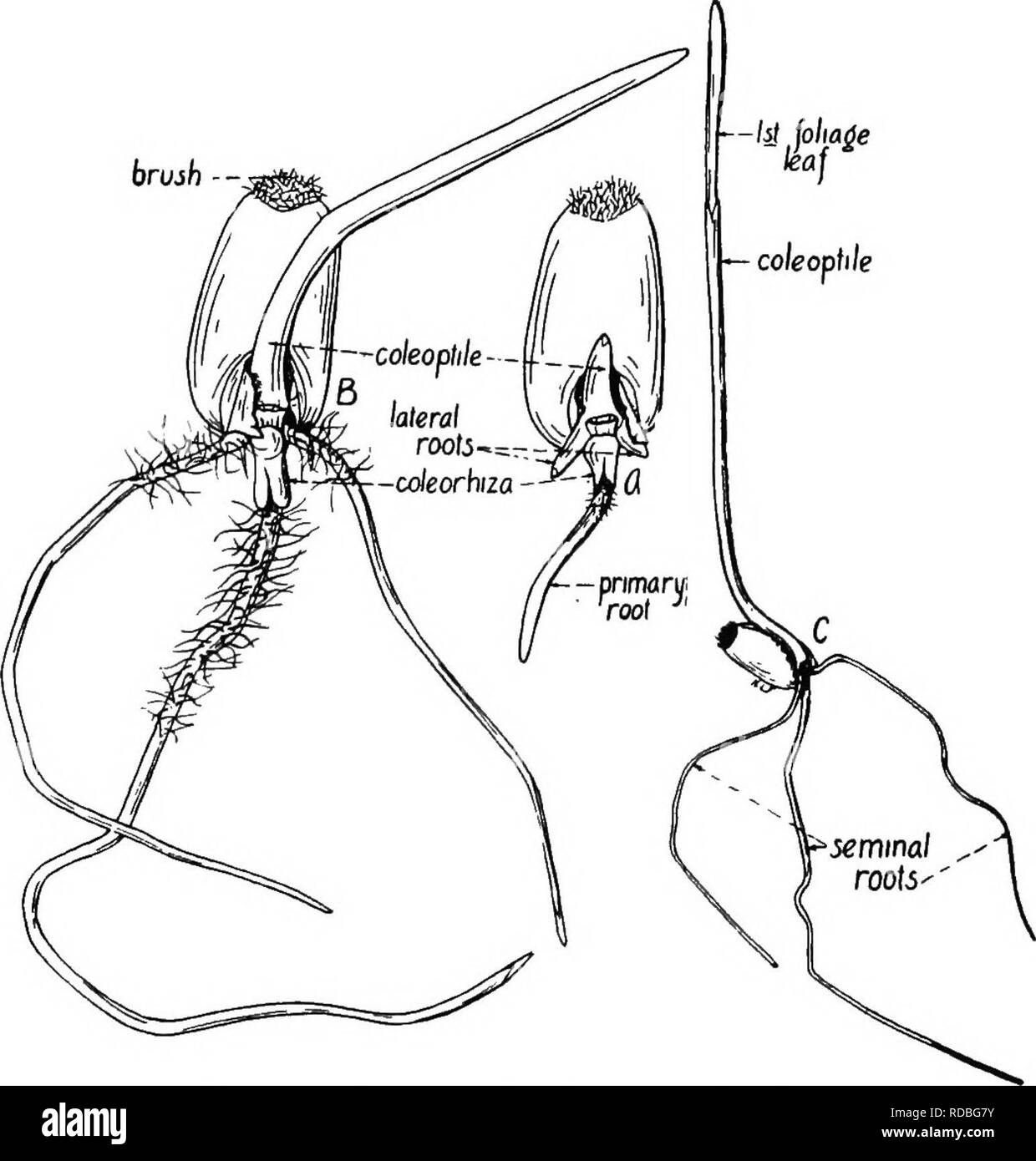


The Botany Of Crop Plants A Text And Reference Book Botany Economic Koots Ii Branches Of Seed Roots But From Stems Or Leaves Are Called Adventitious Roots Hence The Fibrous



Plant And Soil Sciences Elibrary Print Lesson
Some roots, called adventitious roots, arise from an organ other than the root—usually a stem, sometimes a leaf They are especially numerous on underground stems, such as rhizomes, corms, and tubers, and make it possible to vegetatively propagate many plants from stem or leaf cuttingsWhat is a tap root?Which is odd one 1 Stomata , reticulate venation , transpiration , chlorophyll , tendril 2 Sepals , petal , stamen , pistil ,petiol;
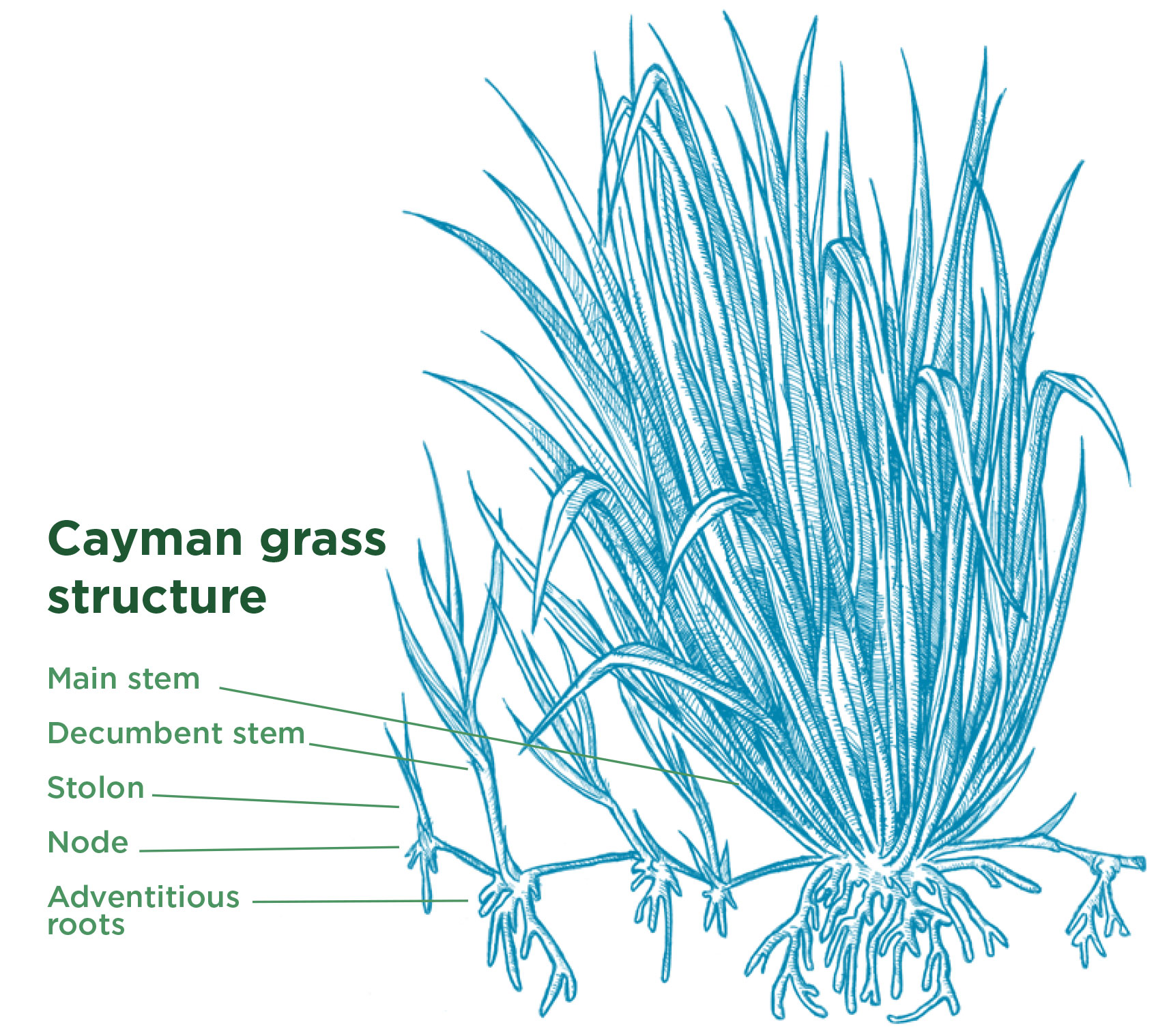


Cayman Grass Brachiaria Hybrid Tropical Seedstropical Seeds


Bil 226 Lecture Nine
Will grow a plant and roots at a node RHIZOME Leaf • Leaf Blade – part of leaf the bends away from stem, usually flat toGive difference between tap root and fibrous root;Leaf, budand adventitious roots Grass roots are generally fibrous and seldom penetrate more than 1 metre below the surface Many species develop rhizosheaths which contain nitrogen fixing bacteria These sheaths act as protective coverings for the roots



Types Of Root System Tap Root The Main Root Which Is Larger And Fast Growing Is Called Tap Root And The Branched Smaller Roots Is Called Lateral Root For Example Beet Root Carrot Sugar Beet Radish Etc Fibrous Root No Main Root All The Roots Are Of Same


16 Of 22 15 Corn Prop Roots
(in words) why are petals colourful?A primary root that persists and remains the dominant root Weed fibrous all roots of approximately equal length and thickness Grass storage a) taproot a root modified for storage a primary root that develops thickened storage tissue (usually the cortex) Beet storage b) tuberous (fleshy)Adventitious roots are the roots of the mature grass plant The seminal roots will disappear The roots anchor the plant to the ground, absorb nutrients and water from the soil, and function as carbohydrate storage tanks (Fig 6, root diagram)



How Bermuda Grass Grows Bermuda Lawn Guide


Canada S Polar Life Plant Biology
Adventitious roots also will form at nodes on the lateral stems stolons, rhizomes and tillers These root systems allow the lateral stems to eventually develop into plants functioning to a large degree independently of the main turfgrass plant Turfgrass roots are fibrous and multibranched Each root tip is covered by a cap that protects the tender


Body



Bouteloua Gracilis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


The Pin1 Family Gene Pvpin1 Is Involved In Auxin Dependent Root Emergence And Tillering In Switchgrass



Grass Guide Trim



Kikuyu Cenchrus Clandestinus For Dryland Salinity Management Agriculture And Food



The Plant S True Brain Plant Physiology
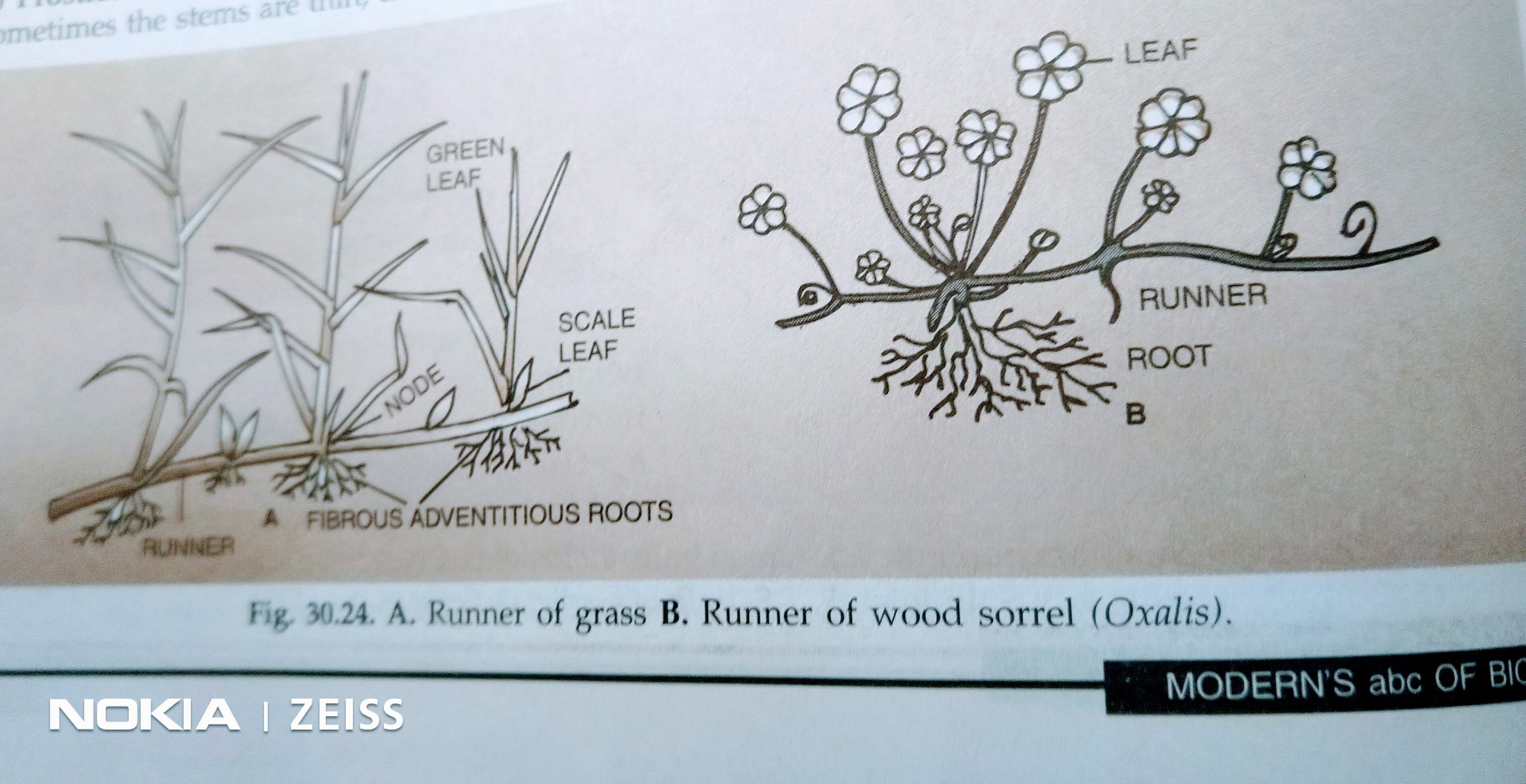


19 10 19 Some Weak Stemmed Plants By Hema Sampath Medium



Summer 16 Cbt110 The Roots Root Is The Organ Of The Plant Originates From The Radicle Of The Embryo The First Root That Comes From A Plant Is Called Ppt Download


Horizontal Tillers Perennial Grass Growth And Development Passel



Dr Erin E Sparks V Twitter Brace Roots Are A Sub Type Of Adventitious Root See The Word Tree That Sarah And I Made For Her Recent Review Paper To Help Define These
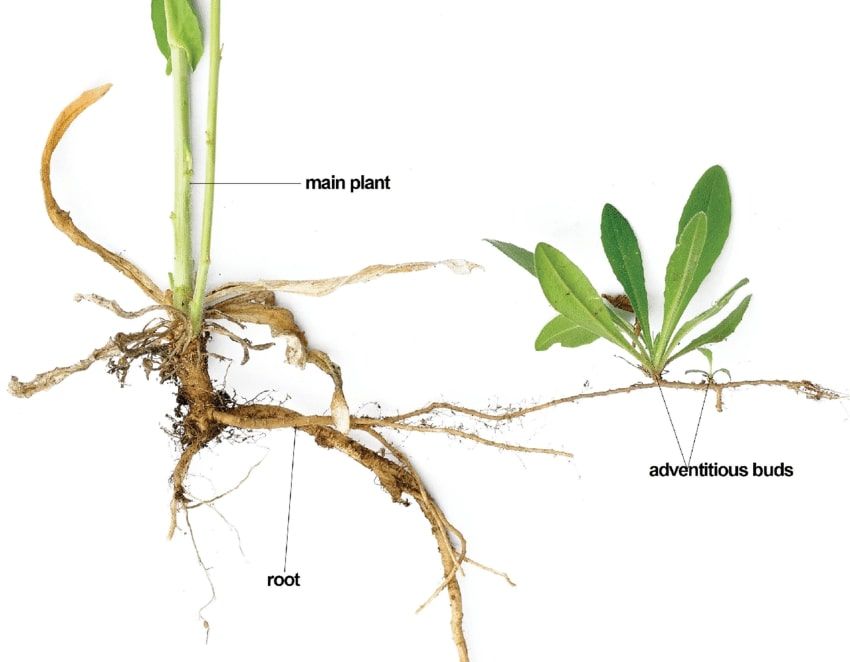



Adventitious Root System Types Modifications And Examples Studiousguy



Monocot Root Leaf Flower And Plants Biology Dictionary


Zoysia Japonica Wikipedia


What Is The Difference Between Fibrous Root And Adventitious Root Lifeeasy Biology Questions And Answers


Big Leaf Is A Regulator Of Organ Size And Adventitious Root Formation In Poplar



Root And Shoot Studies 1 Agriculture2u Com By Subhrajyoti S Horticulture



Structural Organisation In Plants And Animals Ppt Download
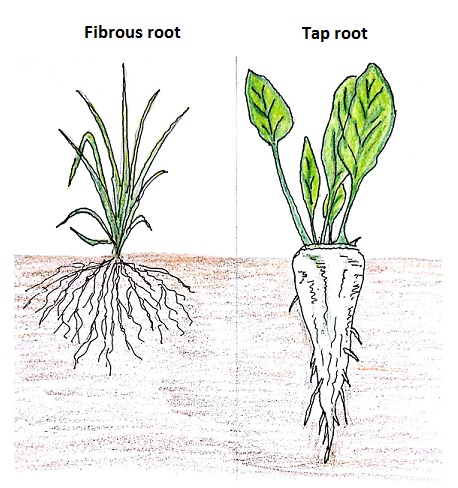


Plants And Root Shoot Systems
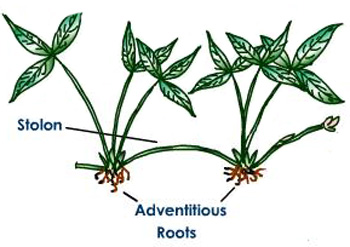


Stolon



Root Definition Types Morphology Functions Britannica



Wetland Indicators



Why Does My Grass Pull Up Easily The Backyard Pros



Adventitious Roots Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Grass Root System Studiousguy



Root Definition Types Morphology Functions Britannica
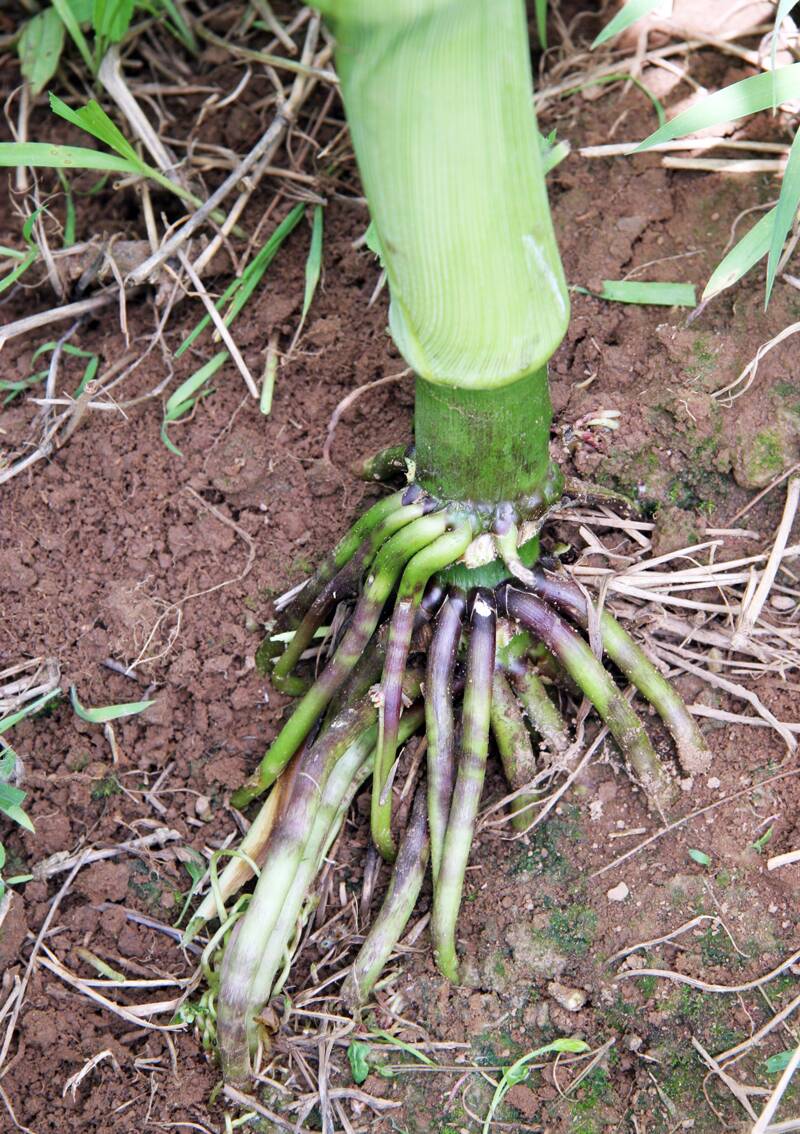



Adventitious Roots



Adventitious Root Growth Information About Plants With Adventitious Roots



Root Morphology



Fibrous Root Systems Consist Of A Mass Of Similarly Sized Roots Plant Mineral Nutrition



Adventitious Roots 1 Driftless Prairies Native Ecosystems



Early Corn Root Development Integrated Crop And Pest Management News Article Integrated Pest Management University Of Missouri


Structure Of Flowering Plants



Morphology Of Flowering Plants Flashcards Quizlet



Kikuyu Cenchrus Clandestinus For Dryland Salinity Management Agriculture And Food


Different Kinds Of Roots



Grass Root System Studiousguy
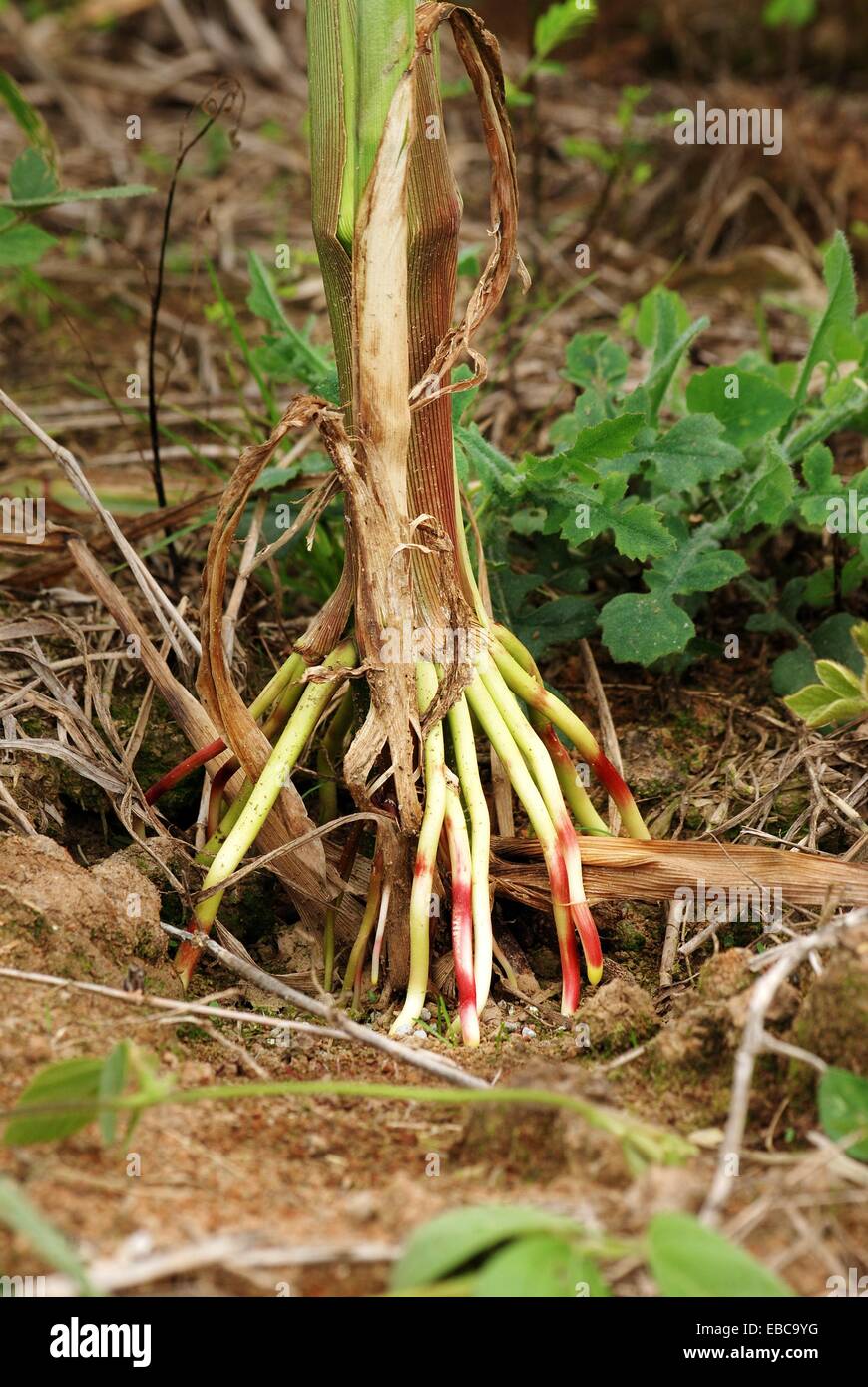



Adventitious Root High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



Solved Can You Please Help Me With A Simple And Short Ans Chegg Com
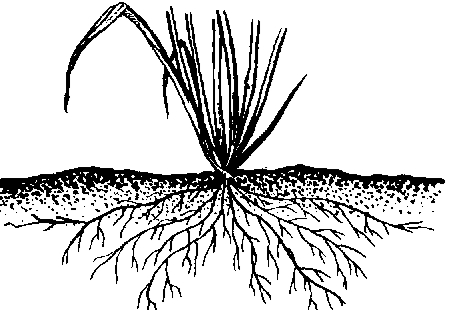


18 Difference Between Taproot And Fibrous Root With Examples Pictures Viva Differences



What Are Some Examples Of Plants That Have Fibrous Roots Quora


Roots The Daily Garden



Vegetative Terminology Part 1



How Long Does Grass Live What How Wonder



Buffalo Grass Weed Identification Brisbane City Council
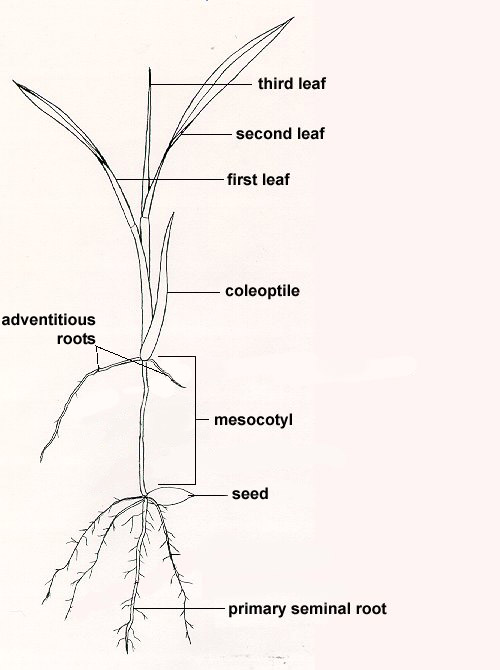


Roots Forage Information System Oregon State University


Adventitious Roots The Daily Garden



Plant Roots Basic Biology
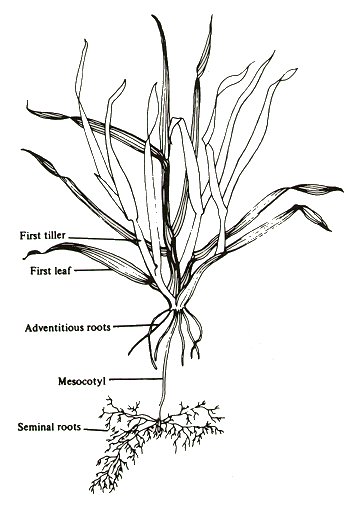


Tillering Forage Information System Oregon State University


Which Type Of Adventitious Root Is Found In Grass Quora
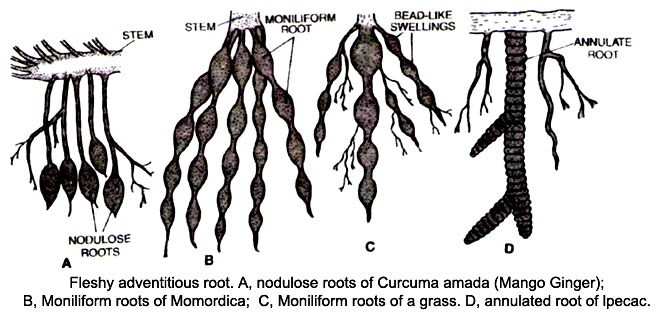


Learn Modified Adventitious Root Meaning Concepts Formulas Through Study Material Notes Embibe Com


Lesson02 Turfs



Adventitious Root Youtube



Pin By Dee Dee Hamilton On Garden Ideas Solutions Biology Plants Roots Taproot
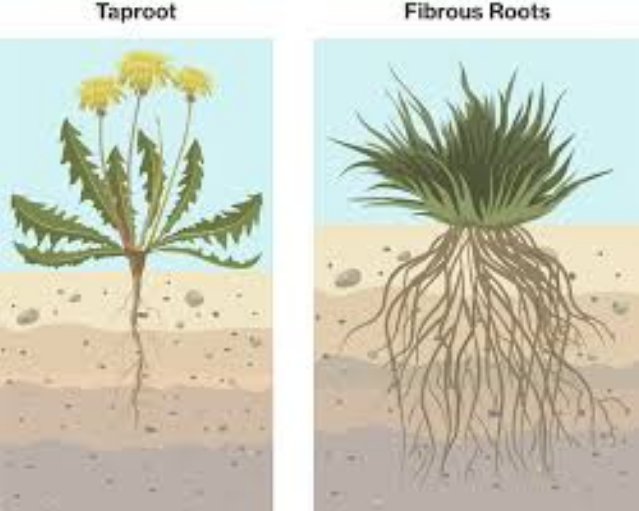


18 Difference Between Taproot And Fibrous Root With Examples Pictures Viva Differences



Mosquito Grass Blue Grama Seeds Bouteloua Gracilis Price 1 45



Difference Between Tap Root And Fibrous Adventitious Root With Comparison Chart Bio Differences


Essentials Of Biology Presented In Problems Biology Couch Grass Showing How The Plant Spreads By Striking Roots From A Reclining Stem Com Roots Showing Prop Roots De Veloped At First Node



Early Corn Root Development Integrated Crop And Pest Management News Article Integrated Pest Management University Of Missouri


Brachiaria Hybrids New Forage Alternatives



Turfgrass Physiology



Turfgrass Physiology
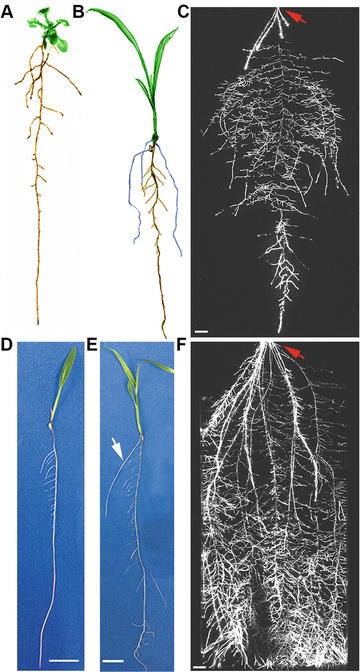


Setaria Viridis A Model For Understanding Panicoid Grass Root Systems Springerlink



Adventitious Roots Stock Illustration


The Physiology Of Adventitious Roots Plant Physiology



Root And Shoot Morphology Of A Adventitious Rootdeficient And B Download Scientific Diagram



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿